Chipset
Chipsets
The chipset
usually contains the processor bus interface, memory controllers, I/O
controllers and more. All the circuits of the motherboard are contained within
the chipset.
When IBM
created the first PC motherboards, it used several separate chips to complete
the design. Besides the processor and optional math coprocessor, many other
components were required to complete the system. These other components
included items such as the clock generator, bus controller, system timer,
interrupt and DMA controllers, CMOS RAM and clock and keyboard controller.
In 1986, a
company called chips and technologies introduced a component called the 82C206-
the main part of the first PC motherboard chipset. This chip included the
functions of the clock generator, Bus controller, System Timer, Interrupt
controllers and DMA controller. Four other chips with 82C206 act as buffers and
memory controllers, thus completing virtually the entire motherboard circuit
with five total chips. This first chipset was called the CS8220 chipset by
Chips and technologies. This was a revolutionary concept in PC motherboard
manufacturing. It reduced the cost of building a PC motherboard and also made
designing a motherboard much easier. The reduced component count make the
boards had more room for integrating other items formerly found on expansion
cards. Later the four chips supporting the 82C206 were replaced by a new set of
only three chips, and the entire set was called the New Enhanced AT (NEAT)
CS8221 chipset. This was later followed by the 82C836 single chip AT (SCAT)
chipset.
Fig: Motherboard with NEAT chipset for the Intel 80286
Intel
chipsets
Intel
introduced the 420 series chipsets along with its 486 processor in April 1989.
Intel has used two distinct chipset architectures: a North/South Bridge
architecture and a newer hub architecture. All chipsets introduced from the 800
series on use the hub architecture.
Intel
Integrated Graphics Architecture
Intel began
producing motherboard chipsets with integrated video starting with the 810
chipset. By building the graphics directly into the motherboard chipset, no
other graphics chip or video memory was required. Many of the chipsets
including integrated graphics also support either AGP or PCI Express video
slots for adding graphics card. With the release of the 845 series chipsets
with integrated video, Intel implemented what it called Extreme Graphics
Architecture. This architecture supported 3D graphics, featuring the following
four technologies aimed at improving 3D rendering speed and quality:
·
Rapid Pixel and Texel Rendering Engine- Uses pipelines to overlap 2D and 3D operations,
provides 8x data compression to improve the use of memory bandwidth, and
features a multitier cache for 3D operations.
·
Zone Rendering-
Reduces memory bandwidth requirements by dividing the frame buffer into
rectangular zones, sorting the triangles into memory by zone, and processing
each zone to memory.
·
Dynamic Video Memory Technology- Manages memory sharing between the display, applications,
and operating system depending on the memory requirements of the programs
running.
·
Intelligent Memory Management- Improves memory addressing, display buffer implementation,
and memory efficiency
Intel included its GMA (Graphics
Media Accelerator) 900 in the 915 family of chipsets. It added support for most
of the core 3D features. Intel GMA 950 is a faster version of GMA 900 and is
found in Intel’s 945 chipset family. GMA 950 offers a 400MHz clock speed,
features support for 16:9 wide-screen flat panels, motion compensation for DVD
playback and HDTV playback.
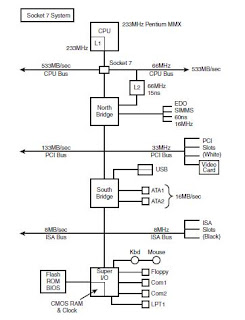
North/South
Bridge Architecture
Most of
Intel’s earlier chipsets are broken into a multitiered architecture referred to
as North and South Bridge components as well as Super I/O chip:
The North
Bridge: It is the
connection between the high speed processor bus and the slower AGP and PCI
buses. North Bridge is sometimes referred to as the PAC (PCI/AGP controller).
Most modern chipsets use a single chip North Bridge: however, some of the older
ones actually consisted of up to three individual chips to make up the complete
North Bridge Circuit.
The South
Bridge: It is the
bridge between the PCI bus and the even slower ISA bus. It also contains dual
ATA/IDE hard disk controller interfaces, one or more USB interfaces, CMOS RAM
and real time clock functions.
The Super
I/O chip: It’s a
separate chip attached to the ISA bus that is not really considered part of the
chipset and often comes from a third party. The super I/O chip contains
commonly used peripheral items all combined into a single chip. Most super I/O
chips contain the serial ports, parallel port, floppy controller and
keyboard/mouse interface. Most recent
models allow three modes: standard, Enhanced Parallel Port (EPP), and the
enhanced capabilities Port (ECP) modes.
Hub
Architecture
In hub
architecture the North Bridge is called a memory controller hub (MCH) and the
south bridge is called an I/O controller hub (ICH). Systems include integrated
graphics use a Graphics Memory Controller Hub (GMCH) in place of MCH. The ICH and MCH are connected through a
dedicated hub interface. The hub design offers several advantages over the
conventional North/South Bridge design:
§ It’s faster- The Accelerated Hub Architecture
(AHA) interface is twice as fast as PCI.
§ Reduced PCI loading- The hub interface is independent of
PCI and doesn’t share PCI bus bandwidth for chipset or Super I/O traffic. This
improves performance of all other PCI bus connected devices because the PCI bus
is not involved in these transactions.
§ Reduced board wiring- The accelerated hub architecture
(AHA) interface is only 8 bits wide and requires only 15 signals to be routed
on the motherboard, while the direct media interface (DMI) is only 4 bits wide
and requires only 8 pairs of signals. But PCI requires no less than 64 signals
be routed on the board, causing increased electromagnetic interference (EMI)
generation and increased board manufacturing costs.
There are two main
variations on the hub interface:
§ AHA (Accelerated Hub Architecture) - Used by 8xx series of chipsets.
AHA is a 4x (quad clocked) 66MHz 8 bit interface, which has twice the
throughput of PCI
§ DMI (Direct Media Interface) - Used by the 9xx and 3x series
chipsets. DMI is basically a dedicated 4bit PCI Express connection allowing
1GBps in each direction simultaneously.
Intel
810E chipsets
The Intel
810 chipset represents a major change in chipset design from the standard North
and South Bridges. The 810 chipset allows for improvements in system
performance, all for less cost and system complexity. The 810 was later revised
as the 810E with 133MHz processor bus.
The major
features of 810E chipset include
§ 66/100/133 MHz system bus
§ Integrated AGP 2x Intel graphics
§ Efficient use of system memory for
graphics performance
§ Optional 4MB of dedicated display
cache video memory
§ Digital video out port compatible
with DVI specification for flat –panel displays
§ Software MPEG-2 DVD playback with
hardware motion compensation
§ Support for ATA-66
§ Integrated Audio-codec 97 (AC 97)
controller
§ Support for low power sleep modes
§ Random number generator(RNG)
§ Integrated USB 1.1 controller
§ LPC bus for super I/O and Firmware
Hub connection.
§ Elimination of ISA bus.
The 810E chipset consists
of three major components:
Ø 82810E Graphics Memory Controller Hub
(GMCH)
Ø 82801 Integrated Controller Hub (ICH)
Ø 82802 Firmware Hub (FWH)
The 810E
GMCH uses an internal Direct AGP interface to create 2D and 3D effects and
images. The video capability integrated into the 810E chip features hardware
motion compensation to improve software DVD video quality; it also features
both analog and direct digital video out ports, which enable connections to
either traditional TVs or a direct digital flat panel display. The GMCH chip
also incorporates the System Manageability Bus, which enables networking
equipment to monitor the 810 chipset platform.
The 82801
I/O controller hub employs AHA for a direct connection from the GMCH chip. This
is twice as fast as the previous North/South bridge connections that used the
PCI bus, and it uses fewer pins for reduced electrical noise. The ICH also integrates dual IDE controllers,
which run up to either 33MBps or 66MBps. The ICH also integrates Audio code 97
(AC 97) controller and dual USB ports. The AC 97 interface means that
conventional modems and sound cards are not required.
The 82802
Firmware Hub (FWH) contains the system BIOS and video BIOS. The BIOS within the
FWH is flash type memory, so it can be field updated at any time. In addition,
the 82802 contains a hardware RNG (Random Number Generator). The RNG provides
truly random numbers to enable encryption.





Comments
Post a Comment